Looking to the Hour of Code website again it provides students with step by step instruction on how to increase their knowledge and understanding of computer programming and coding. In essence students are developing the computational skills needed for algorithmic solutions to problems. The Angry Birds simulations starts students with basic coding blocks and moves on to more complex ideas such as using repeat blocks to avoid lengthy coding formulas.
This tool could easily be integrated into the classroom for use with individual students or small groups and would meet the criteria under the digital curriculum in the strands for defining, designing and implementing processes and production skills.
Thursday, 7 May 2015
Visual Literacy
According to Younie, Leask and Burden (2015, pg.55) visual literacy "combines the use of a variety of visual products (lists, tables, graphics, graphic organizers, concept maps, mind maps, argument maps, timelines and system maps) with teaching, learning and assessing processes, and creates interconnections of visual, oral, written, visual representation, numeracy and technological literacy." The strategies used through visual literacy help students to develop a greater sense of mastery and the ability to explore numerous cognitive reasoning strategies including classification, comparative thinking, evaluation and design thinking.
Visual literacy is important in the 21st century as more and more often we are subjected to an influx of visual materials. It is important that students become fluent in their ability to use, understand, comprehend and create visual literacy pieces.
This blog has previous addressed the benefits of visual learning through the use of infographics and the same principles apply here.
Visual literacy is important in the 21st century as more and more often we are subjected to an influx of visual materials. It is important that students become fluent in their ability to use, understand, comprehend and create visual literacy pieces.
This blog has previous addressed the benefits of visual learning through the use of infographics and the same principles apply here.
Computational thinking ... is it abstract?
There are numerous definitions of what computational thinking actually is and how it can be encompassed in all areas of the curriculum, not just the digital curriculum. Some of the components examined here include abstraction, patterning, algorithms and decomposition. The development of these skills will ensure students have a repertiore of problem solving skills which will assist them across the curriculum. Thinking Myself provides a range of explanations, examples and activities that students can complete to develop their knowledge and understanding of computational thinking strategies.
Teachers who encompass a pedagogy which allows students to explore together in a collaborative manner will be providing a classroom which meets numerous criteria outlined by the national curriculum. Criteria such as:
Google provide a number of resources for the effective instruction and improvement of students skills in this area. They also provide information about the four areas of computational thinking. According to Google:
- Decomposition refers to the ability to break a problem down into smaller more manageable chunks. In doing so it often becomes apparent that algorithms or patterns can be used to create solutions to a problem.
- Patterning can be used to identify similarities or differences that can assist in solving problems. Patterns can often lead to the use of algorithms in providing solutions.
- Abstraction allows the problem solver to sift through the information provided and decipher its relevance to the solution required. It allows for generalisations to be made that can be used for solving further problems.
- Algorithms use a step by step process which often includes the use of patterns and decomposition.
Barr and Stephenson (2011, pg. 52) go on to describe that a classroom conducive to computational thinking can be characterised as one where:
- Teachers and students increase their use of a vocabulary appropriate to describing problem solving strategies.
- A recognition that there will be failed attempts throughout the problem solving process and that these opportunities can lead to a more successful path to solution.
- Team work among students with activities and resources that will allow them to develop their skills in all areas of decomposition, patterning, abstraction and algorithms.
Teachers who encompass a pedagogy which allows students to explore together in a collaborative manner will be providing a classroom which meets numerous criteria outlined by the national curriculum. Criteria such as:
- design, create, manage and evaluate sustainable and innovative digital solutions to meet and redefine current and future needs.
- use of computational thinking and the key concepts of abstraction; data collection, representation and interpretation; specification, algorithms and implementation to create digital solutions.
- Confidently use digital systems to efficiently and effectively automate the transformation of data into information and to creatively communicate ideas in a range of settings.
- apply protocols and legal practices that support safe, ethical and respectful communications and collaboration with known and unknown audiences.
- apply systems thinking to monitor, analyse, predict and shape interactions within and between information systems and the impact of these systems on individuals, societies, economies and environments.
Using authentic learning environments will allow students to apply their learning to their own real world contexts. Activities such as the tuckshop challenge is a great example and allows for the application of multiple key concepts and aims.
Tuesday, 5 May 2015
Cracking the code.... rgb = offset = var = size = = =
Coding has always seemed like a nightmare of letters and numbers that to a normal person like me makes NO sense at all! I always knew it was there in the background and that everything had a particular meaning but using activities with a step by step approach such as Code Monster makes it easy to understand in small chunks. Stepping through this website has, and will do the same for the students I teach, allowed me to increase my abilities to create digital technologies and resources. One of the main benefits of using a program such as Code Monster is that it allows students to see both sides of the coding at the same time, that they can see the changes they are making side by side so the coding they are changing shows right in front of them. This makes it more realistic and comprehendible for students.
Once again actually allowing students to DO IT will have the best possible outcome.
Another great site to use is the Khan Academy. It has a similar layout but break the process down into a small tutorial followed by a step by step challenge to be completed. Students can accumulate points and step through a range of activities and challenges.
For the younger children an app such as Scratch Jnr is a great way to introduce coding. It provides a platform that allows them to have fun, create characters that they can relate to or interest them and then tell a story using coding blocks. Students from age 5 could easily learn to use this app and in either small group tasks or individually could create some amazing stories and tales. Working in small groups may help with the creation of ideas and allow students to explore further than they might if working on their own.
It could be interesting to have students in the lower grades create a presentation of their show and tell which used an app such as Scratch Jnr. This could then be presented to the class rather than students having to personally do it. An activity such as this would help students develop their knowledge and understanding in the digital systems sub strand and also develop their processes and skills in the collaborating and managing sub strand.
Once again actually allowing students to DO IT will have the best possible outcome.
Another great site to use is the Khan Academy. It has a similar layout but break the process down into a small tutorial followed by a step by step challenge to be completed. Students can accumulate points and step through a range of activities and challenges.
It could be interesting to have students in the lower grades create a presentation of their show and tell which used an app such as Scratch Jnr. This could then be presented to the class rather than students having to personally do it. An activity such as this would help students develop their knowledge and understanding in the digital systems sub strand and also develop their processes and skills in the collaborating and managing sub strand.
Digital Technologies - Infographics and Binary Numbers
When I first looked at the concept of binary numbers I found it confusing and hard to follow, but the more I played with the games and watched the you tube clips about it the more it made sense (I did have to switch off for octal and hexidecimal for a while until I got the hang of things, I was getting too confused!!). Taking a hands on approach and creating a resource I could use with students helped develop my understanding. I think this is an important point to remember when dealing with digital technologies, some of the ideas and concepts are abstract and hard to grasp. For this reason it is important that teachers ensure students have activities and resources that they can use to explore with their hands and their minds. Practical experience using games, concrete materials and simpler terms will help students to grasp the concepts and processes teachers are tying to share with students. From then students will have the opportunity to develop a deeper knowledge and understanding of the relevant technologies, which will help them to develop solutions to problems they may not otherwise have been able to find.
INSERT IMAGES FOR BINARY WORKSHEETS AND CARDS
Creating ways to show students information in a way that is clear, makes sense and is easily remembered is important. An infographic is a quick and easy way to do this. It also provides a good way for students to convey the information they have learned and show the skills they are continually developing. Using a program such as http://www.easel.ly/ will provide students with a range of options to use and explore. This way of displaying their information will allow them to design, create and manage digital tools.
INSERT IMAGES FOR BINARY WORKSHEETS AND CARDS
Creating ways to show students information in a way that is clear, makes sense and is easily remembered is important. An infographic is a quick and easy way to do this. It also provides a good way for students to convey the information they have learned and show the skills they are continually developing. Using a program such as http://www.easel.ly/ will provide students with a range of options to use and explore. This way of displaying their information will allow them to design, create and manage digital tools.
Wednesday, 15 April 2015
The Design Process – a reflection to consider
Initial thoughts about starting the technology design
challenge were not overly positive ones, I had preconceived ideas which were
mostly negative. This is probably a common reaction from teachers who have not
had the opportunity to really engage in the process and learn about the
benefits for educating students today. We have an ever changing globalised
world to educate children in and it’s important that their learning encompasses
the best of this and teaches them how to deal with the everyday world they
experience in a safe and exciting way. The technology design process does this!
Immersing students in a project that excites them and educates them at the same
time is powerful. The Design and Technologies and Digital Technologies
curriculum focuses on creating students who are active and informed in
sustainability, ethics, are socially responsible, can work collaboratively or
individually, can critically analyse and think and have the ability to
communicate on a number of different levels.
At the beginning of the process the planning phases can be a
little arduous and drawn out if the students were to complete them all by
themselves, however, it can be made fun and exciting and adapted to suit any
age level. Simple planning
sheets which are age appropriate could help to alleviate concerns that
students may lose focus. I believe the whole design process whilst it has definite
stages needs to be a very flexible and open ended process which can allow students
to come up with a range of different solutions and ideas to address the initial
challenge. Teachers need to make the design challenge age and experience
appropriate and relevant to each classes context.
The design challenge process lends itself to both individual
and collaborative learning and can easily foster both. Even though a challenge
may be presented as individual work, using the peer feedback process involves
students in a collaborative learning situation which can be beneficial on a number
of levels. Peer feedback allows students to learn from each other, rather than
just the teacher. Students will engage in meaningful discussions and provide
each other with constructive comments about ways to improve a project whilst
also finding the points that have been done well and celebrating successes.
However, students still
need to include constructive criticism in order to increase learning and
engagement. Merely saying that everything is great does not extend
learning and thinking and allow for growth in a project. It is important that
this learning process is monitored closely to ensure students really understand
its purpose and how to effectively and courteously take part in the process.
Another critical component in the design process is being
able to make informed and educated decision about the final project or
solution. Educating students on how to do this gives them tools to be able to
reason and justify their decisions, not only in their project but in their
everyday decisions. The use of a decision making matrix is a great tool for
students to have and use. In my design challenge I used an existing template and
used it in a different way to suit my needs. However, throughout my readings
and research I came across the following template which I feel provides a
perfect example that could easily be incorporated into the classroom for
student use.
Taken from: Teepee Consulting. (2011) Higher Order Thinking for Gifted and Talented Students. [Powerpoint Slides]. Retrieved from https://moodle.cqu.edu.au/mod/page/view.php?id=13721.
Overall the technology design process provides students with
immense benefits in their learning but does require teachers to adjust their
teaching pedagogies. Teachers become more of a facilitator rather than
dictator. Students need to be allowed to explore and investigate to create
their own learning. Teachers will be required to carry out more forward
planning to ensure the resources that students may need are available and
depending on their imaginations and creativity this could be a lot or a little.
Teachers will also have to adjust to the type of environment that students need
in order to be creative, it may not always be an ordered, tidy classroom that
facilitates creativity! For me this will be challenge in itself. It is
important to allow students the freedom to explore and create their own
understandings, and to experiment with this new found knowledge in order to
learn how it is relevant to their world and can help them to create a better
and more sustainable community. The answers will be in the solutions they
uncover throughout their explorations.
Sunday, 12 April 2015
How do children learn about technology..... let's twitter
How do children learn about technology... well here are some thoughts about it from twitter.....
#edcu12039 Tweets
Children learn about technology by getting in there are really investigating about it, using it and exploring what it can do in their world.
When planning activities around technology teachers should use real world situations that allow students to discuss and investigate their surrounding communities. Hands on, creative situations should be developed in order to allow students to assimilate this new knowledge with existing schemas. Investigation and exploration will develop students understanding of technology, what it is and what it can do for us.
Twitter is an example of an avenue that allows student to communicate their thoughts in a concise and practical manner. Tweets have a limited number of characters (140), can be tracked using the hashtags and collected just as I have done above. This could allow for a whole class discussion to occur when and where students are able to. It gives them time to reflect on learning, investigate and then put their thoughts down on paper. Could it be embedded into a homework program....students must provide a tweet at the end of the day/week about their learning on particular topic covered in class????
#edcu12039 Tweets
Children learn about technology by getting in there are really investigating about it, using it and exploring what it can do in their world.
When planning activities around technology teachers should use real world situations that allow students to discuss and investigate their surrounding communities. Hands on, creative situations should be developed in order to allow students to assimilate this new knowledge with existing schemas. Investigation and exploration will develop students understanding of technology, what it is and what it can do for us.
Twitter is an example of an avenue that allows student to communicate their thoughts in a concise and practical manner. Tweets have a limited number of characters (140), can be tracked using the hashtags and collected just as I have done above. This could allow for a whole class discussion to occur when and where students are able to. It gives them time to reflect on learning, investigate and then put their thoughts down on paper. Could it be embedded into a homework program....students must provide a tweet at the end of the day/week about their learning on particular topic covered in class????
Decisions, decisions, decisions.....???????
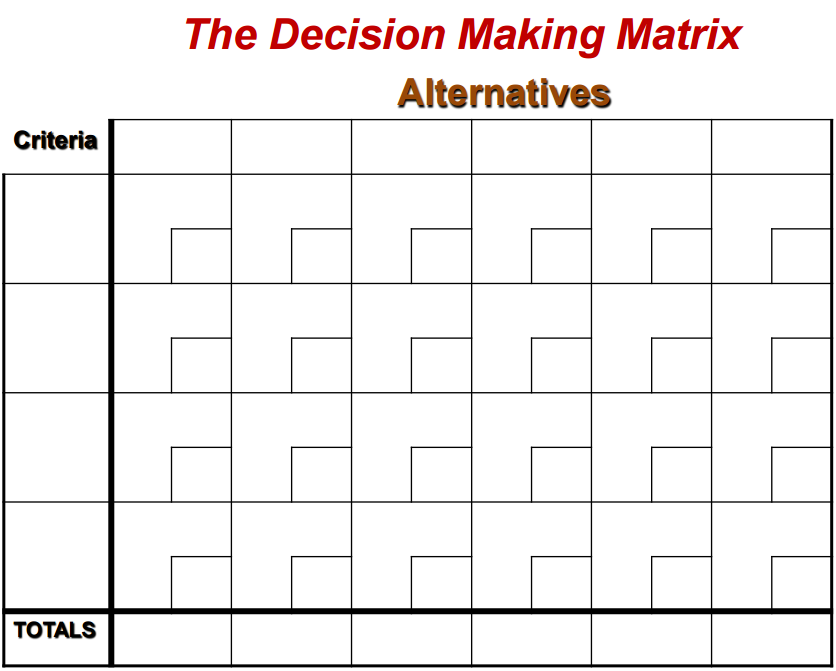
Sometimes making a final decision can be very difficult, especially when involved in group work. So how can that be done. Using a decision making matrix is the answer. Initially I thought this would be a very arduous process but I was wrong. Using a template such as this one....
allows the users to comprehensively and accurately decide on the final choise for their projects in a matter of minutes.
It requries students to
I did modify my use of the table slightly to have designs listed on every second row to allow for totals of each design to be shown in the same table rather than create the table a second time which showed the totals rather than the rankings. Mine have all been combined into the one table. I feel that this gives a simpler overview of things rather than swapping between two tables if changes needed to be made.
Some of the benefits of using a decision making matrix include:
allows the users to comprehensively and accurately decide on the final choise for their projects in a matter of minutes.
It requries students to
- List in the columns the factors on which to base their decisions such as cost, size, purpose etc.
- On the left each row is labelled with the designs/solutions they are choosing from.
- Each factor must be given a raking from 1-5 (1= not important to 5=extremely important) and different factors can have the same value.
- Each of the designs must then be given a ranking as to how well it demonstrates/reaches the factors.
- Multiply each of the answers with the corresponding design and factors rankings to calculate an amount.
- Add all the amounts in each row to obtain a total on the right hand side.
I did modify my use of the table slightly to have designs listed on every second row to allow for totals of each design to be shown in the same table rather than create the table a second time which showed the totals rather than the rankings. Mine have all been combined into the one table. I feel that this gives a simpler overview of things rather than swapping between two tables if changes needed to be made.
Some of the benefits of using a decision making matrix include:
- Unbiased opinions
- Allows for matching comparisons of numerous design at the same time
- Numerous factors can be accounted for in one matrix
Design Process - the beginning.
I think the design process is really aimed at creating interesting and creative classrooms and we know from research that this is best done through a collaborative approach. Creating small groups based on similar interests will spark student curiosity and giving them a project that they can really relate to and delve into. Initially I had thought that this project would be done individually but going through the process I think small groups will allow students to be more creative with each other and "bounce" ideas off each other. It will also allow for the collection of more materials for the final project between group members if required. This change in though has quite surprised me as I thought individual works would be more appropriate before beginning and reading my peer feedback.
The peer feedback process has also surprised me! I began the process with a negative preconceived idea of how the process would fail...... My group members have open, honest and helpful. I think that working in groups online still generates a number of issues with reliability, completing tasks on time (I have failed at this over the last couple of weeks and know that feeling of letting my peers down) and sharing of work loads. However, in a classroom environment where all these facets can be monitored, managed and facilitated it should work well. Students will learn how to give constructive feedback. That is, being positive all the time is not going to help learning and negativity should also be left out. With the inclusion of ideas to support learning and praise for ideas which are well conceived.
The peer feedback process has also surprised me! I began the process with a negative preconceived idea of how the process would fail...... My group members have open, honest and helpful. I think that working in groups online still generates a number of issues with reliability, completing tasks on time (I have failed at this over the last couple of weeks and know that feeling of letting my peers down) and sharing of work loads. However, in a classroom environment where all these facets can be monitored, managed and facilitated it should work well. Students will learn how to give constructive feedback. That is, being positive all the time is not going to help learning and negativity should also be left out. With the inclusion of ideas to support learning and praise for ideas which are well conceived.
Tuesday, 17 March 2015
Concept Mapping... the why and the how.
What is concept mapping and why would students and teachers use it in the classroom. Surely it is time consuming and a waste of valuable classroom time that could be spent reciting maths facts.......
Other theories include:-
Dual coding theory which ensures that there is importance placed on both the verbal and non-verbal cues in the learning process. Therefore, as well as talking about new concepts or knowledge students also have a visual cue in the form of a concept map to assist with their learning.
Schema theory supports the idea that students need to have prior information to associate new information with or create a new schema for new information. The use of a concept map in the classroom will help students associate information in the correct schema or help them generate new schemas to assimilate information.
Cognitive load theory suggests that students can retain new information if there is an abundance of information to be learned at one time. Therefore, the concept map would assist teachers in planning lessons and curriculum content to be taught to ensure that information is passed on to students at an appropriate time and in conjunction with other relevant information.
According to Novak, new concepts are acquired either by discovery learning or receptive learning. Discovery learning is the type of learning typically undertaken in the home and up to the time children begin formal schooling. Children are involved in a range of activities whereby they learn the skills they need to complete relevant tasks such as learning to communicate and investigating the world around them. Receptive learning is that which stereo-typically takes place in an educational setting whereby students are given information or concepts that they need to learn in a variety of content areas and contexts.
Concept mapping tools also fit neatly within a constructivist approach to learning where the following seven principles are important:-
WELL, I am hear to tell you that no that is not the case, it is most certainly a valuable tool in organising, planning, assessing and learning.
Looking back at the history of concept mapping, Joseph Novak was a professor who understood the importance of this valuable tool back in the 1960's and has researched its benefits and value for the classroom and teacher. An article from Stanford University (http://web.stanford.edu/dept/SUSE/projects/ireport/articles/concept_maps/ConceptMapsOnlineLearningEnvironment.pdf) goes on to explain the theories, ideas and benefits of concept mapping which I have summarised below.
What does a concept map look like?
They contain ideas that are represented in circles or blocks with lines between them to show relationships.
What are the advantages of using them?
Online concept maps have a variety of advantages including:
- they are easy to correct, manipulate or adapt
- can be converted into multiple formats
- can be sent to teachers, friends or peers for immediate feedback
- shows levels of understanding for the particular concept
What theories support the use of concept mapping tools to enhance learning?
There are a number of theories that support these tools and Joseph Novak investigated the theories of David Ausubel in his Meaningful learning theory. This theory proposed that "learning new knowledge is dependent on what is already known. In particular, new knowledge gains meaning when it can be largely related to a framework of existing knowledge rather than being processed and stored in isolation according to more or less random criteria."Other theories include:-
Dual coding theory which ensures that there is importance placed on both the verbal and non-verbal cues in the learning process. Therefore, as well as talking about new concepts or knowledge students also have a visual cue in the form of a concept map to assist with their learning.
Schema theory supports the idea that students need to have prior information to associate new information with or create a new schema for new information. The use of a concept map in the classroom will help students associate information in the correct schema or help them generate new schemas to assimilate information.
Cognitive load theory suggests that students can retain new information if there is an abundance of information to be learned at one time. Therefore, the concept map would assist teachers in planning lessons and curriculum content to be taught to ensure that information is passed on to students at an appropriate time and in conjunction with other relevant information.
According to Novak, new concepts are acquired either by discovery learning or receptive learning. Discovery learning is the type of learning typically undertaken in the home and up to the time children begin formal schooling. Children are involved in a range of activities whereby they learn the skills they need to complete relevant tasks such as learning to communicate and investigating the world around them. Receptive learning is that which stereo-typically takes place in an educational setting whereby students are given information or concepts that they need to learn in a variety of content areas and contexts.
How can teachers use it as a learning tool?
The article from Stanford University states that "it serves as a template to aid in the organization and structuring of knowledge even though this knowledge is built up piece by piece." Concepts maps help students to put together a visual representation of their learning where they can relate all the bits of information together to develop deeper understanding of the layers involved with the concept they are learning. They can clearly see relationships between new information and old. That is they can apply the information to the relevant schemas they have already developed and create new ones when necessary.Concept mapping tools also fit neatly within a constructivist approach to learning where the following seven principles are important:-
- Knowledge and beliefs are formed with the learner
- Learners personally imbue experiences with meaning
- Learning activities should cause learners to gain access to their experiences, knowledge and beliefs
- Learning is a social activity that is enhanced by shared inquiry
- Reflection and metacognition are essential aspects of constructing know;edge and meaning
- Learners play a critical role in assessing their own learning
- the outcomes of the learning process are varied and often unpredictable
Can concept maps be used as an assessment tool as well as a learning tool?
Absolutely. Concept maps can be used to follow and evaluate student learning while creating the documentation needed by teachers to support their marking or grading of students work. It is a great way for students to self assess or peer assess each other by looking for similarities and differences in their concept maps. This can also lead to discussion points where further learning and justification can take place. Teachers can use concept maps to see the depth of understanding a student has in relation to a particular concept. It will also help to show misconceptions and the areas students are struggling with.
For this to be an effective tool for assessment students must first understand the point and ways of working with concept maps, there must be a comparable "expert" example to mark from and a set of criteria for the marking. Stanford University describes three characteristics required for concept mapping to be used as an effective assessment tool:-
- A task that requires students to give evidence of possession of knowledge structure of a domain.
- A format for student's response.
- A scoring system by which concept maps produced by students can be evaluated consistently and accurately.
What about planning for the classroom?
Teachers have a variety of methods at their disposal for planning and creating lessons. However, the benefits of using a concept map are numerous. They can be used individually or in groups and can track the ideas, key words, concepts, images needed or processes the teacher wants to use in the classroom. It also gives teacher the tools required to solve complex problems, to organise teaching content to ensure that all areas needed to be covered under the curriculum can be included in an orderly fashion without missing important components. It provides a comprehensive storage package for all media and content the teacher may require.
SO, overall there are are a multitude of reasons to support the use of online concept maps as a teaching, planning, learning and assessing tool. The benefits seems endless and provide an interesting and effective tool to manage student learning.
Monday, 9 March 2015
Technology, Design, Curriculum...... How does it all fit together?
The technologies curriculum is broken into two strands:
- Design and Technologies
- Digital Technologies
These two areas combine to create a comprehensive technology program for students. Under the Design and Technologies strand we see a focus on helping students to consider sustainability, ethics and to develop a social responsibility for the future generations. Throughout the Digital Technologies content we see a shift towards computational thinking and using collaboration and communication to achieve a desired result.
Technology has a been given a number of definitions over the years however, in today's educational context the definition described by Volti (2008) and written about by Jose Anazagasty (2014) is most appropriate. "A system produced by humans that employs knowledge and organisation to make objects and developed techniques for the specific achievement of goals."
So we can see that technology is no longer just artefacts or items we can put our hands on but rather the combination of these items and the planning and processes that go with them in a social context. The social element is becoming increasingly important.
 So .... What pedagogy will be needed?
So .... What pedagogy will be needed?
Students will need to carry out a number of tasks and employ a range of strategies to develop a concrete understanding of the Technology Curriculum. Some of these skills can be described here.
Design Thinking and Computational Thinking ...
What are the differences?
Both types of thinking are centred on finding solutions to problems, but, the way students will go about finding these solutions will be very different when using these two approaches.
Under the design thinking model students will use an exploratory or heuristic approach to finding a solution. Students will be given the opportunity to design, create innovative ideas, apply and evaluate these designs. All the while taking into consideration the effects on society and environment. Students will be able to design and redesign until the end goals are reached.
Throughout the computational thinking process students will use strategies and techniques for problem solving that are basically algorithmic in nature. These processes basically involve collecting and organising data, breaking down issues and problems into components to be worked on by those with the specific skills to do so and looking for patterns and algorithms.
What else is important?
Higher order thinking has proven to be an effective tools in educating students and allowing them to develop a deeper understanding of their content. Robyn Collins outlines the importance of this in her article Skills for the 21st Century; teaching high-order thinking (http://www.curriculum.edu.au/leader/teaching_higher_order_thinking,37431.html?issueID=12910). Collins article goes further to explain three categories for higher order thinking:
- Transfer - students not only need to learn new information but they also need to be able to apply this information in a real world context.
- Critical Thinking - students need to be to take information they have gained and examine that information to decide if it is useful, truthful and relevant to the context they are working in.
- Problem Solving - enables students to come up with solutions to a problem that requires more than just memorising facts or figures.
Collins advises that there are many frameworks available to support the teaching of higher order thinking, however, Blooms is the most widespread. She also provides the following stages to help implement an effective program including higher order thinking:-
- Specifically teach the language and concepts of higher order thinking
- Planning classroom questioning and discussion time to tap into particular higher-order thinking skills
- Explicitly teaching subject concepts
- Providing scaffolding
- Consciously teach to encourage higher order thinking
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)